Quantum Sensing with NV Center in Diamond
Nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers are a prominent platform in the field of quantum sensing and imaging. By measuring changes in NV fluorescence, researchers can harness the sensitivity of NV center’s electron spin states to detect changes in magnetic and electric fields, microwave radiation, and other environmental parameters. NV embedded nanodiamond host particles offer nanoscale sensing resolution, and NV centers can be used for room temperature measurements sensitive to a single electron spin or a few nuclear spins external to the NV center. Scroll down to explore diamond-based quantum sensing applications.
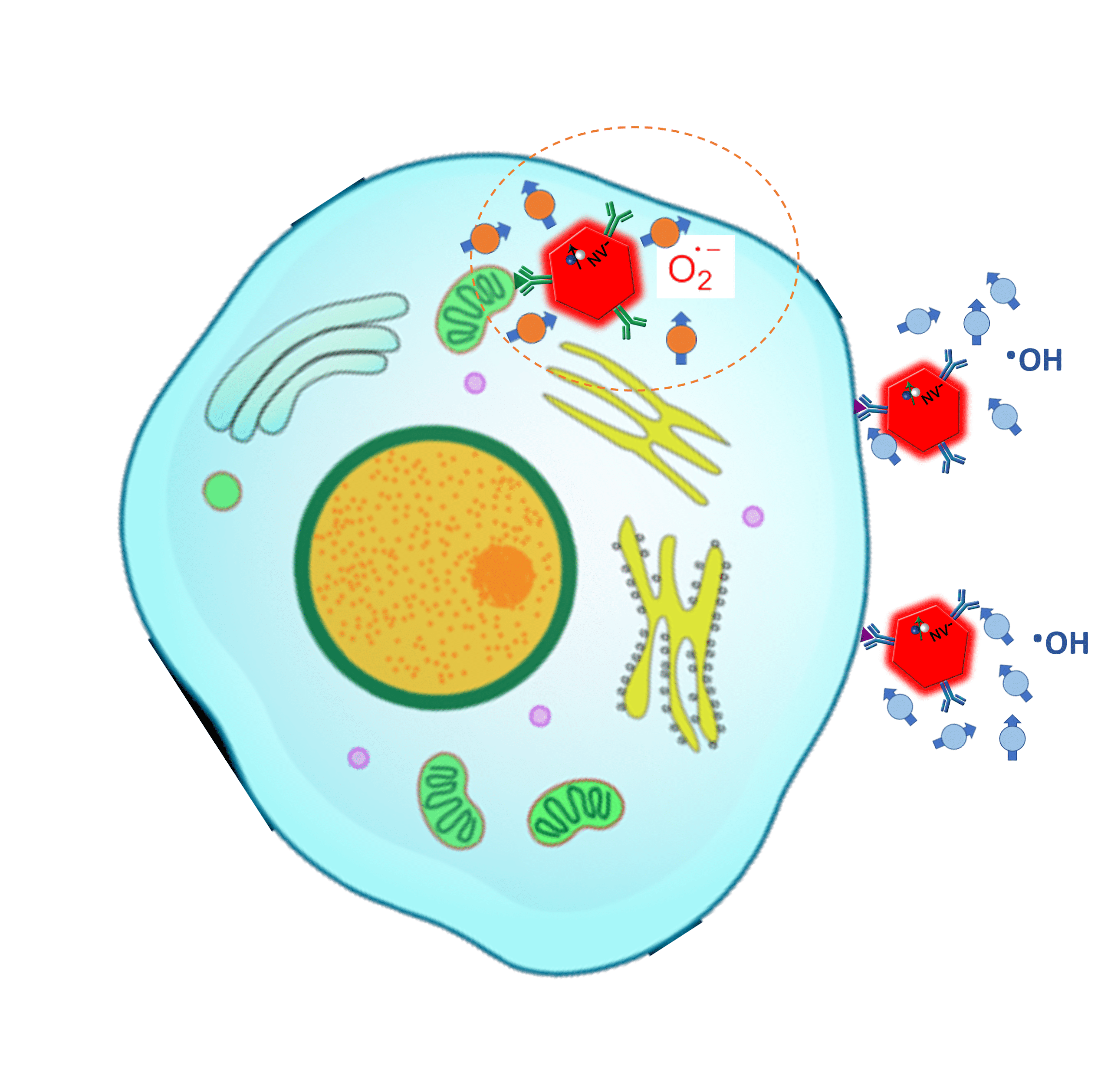
Detection of free radicals by T1-relaxometry
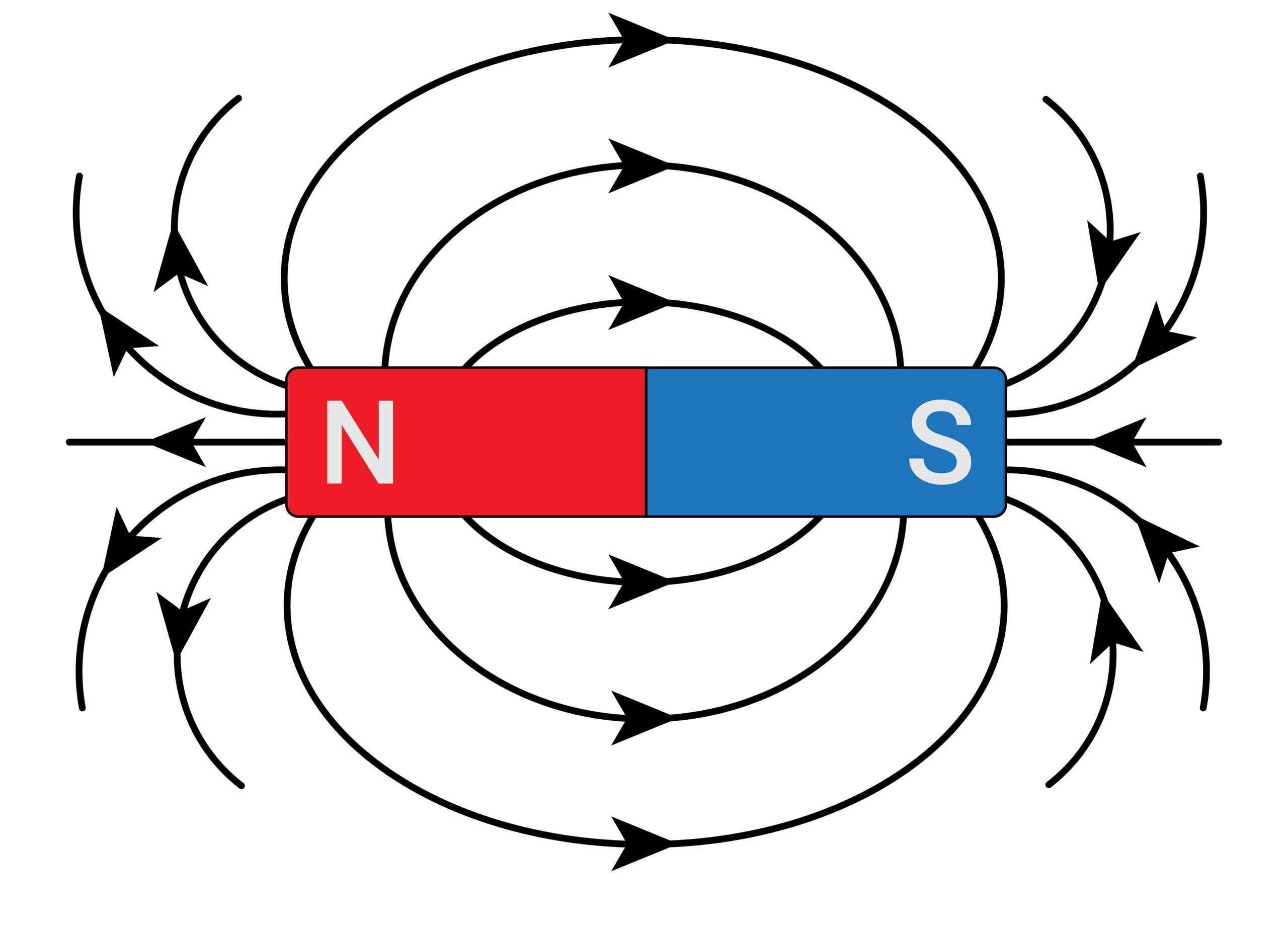
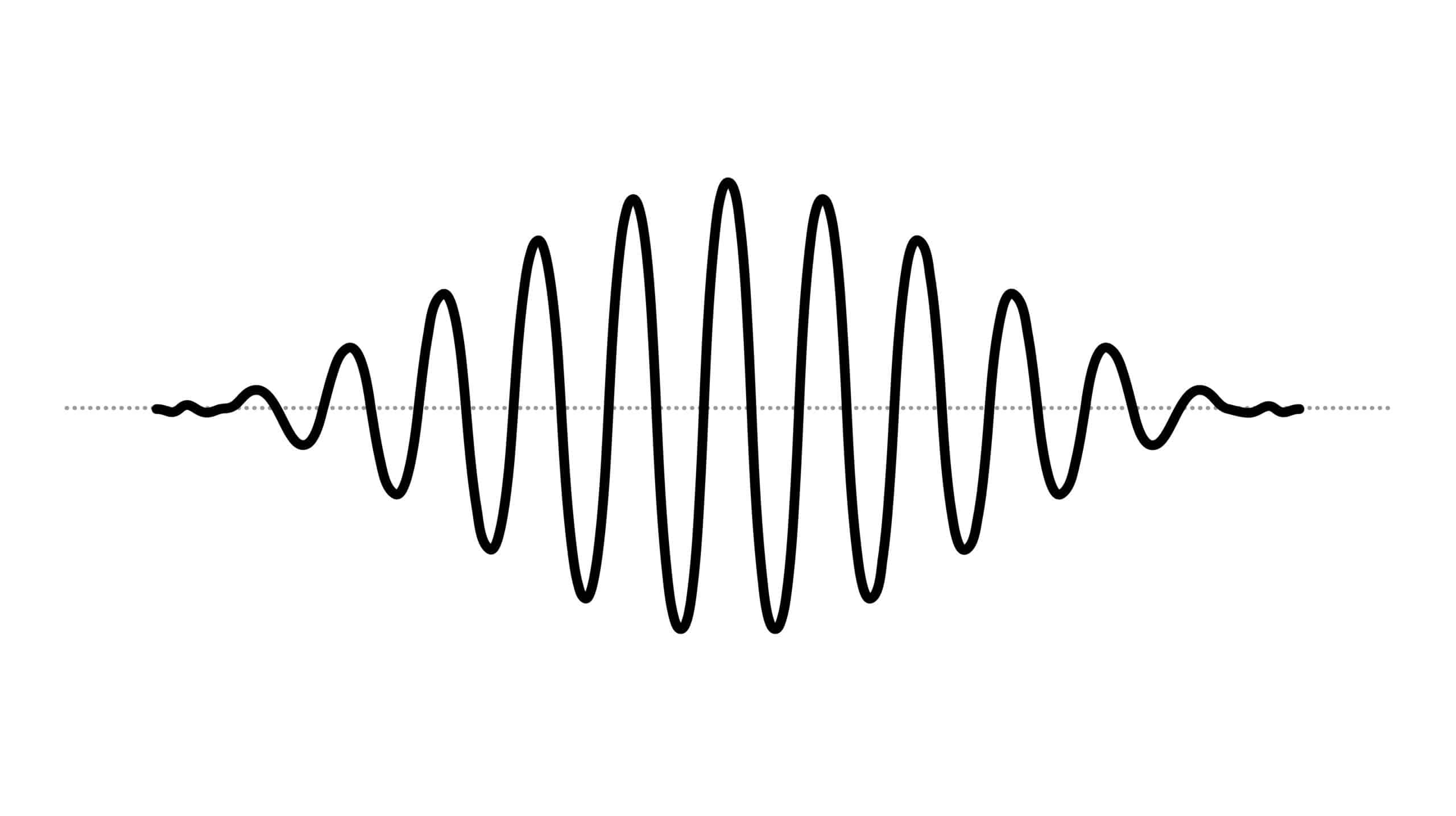
NV T1-relaxometry measures time required to repopulate electron spin states from optically polarized spin states (“bright”) back to their thermal equilibrium states (“darker”). The value of T1 is highly sensitive to the presence of magnetic noise (e.g., paramagnetic species) external to NV. In comparison with conventional methods, T1-relaxometry is capable to reveal free radical concentration at nano/micromolar range and in real-time, as had been demonstrated in numerous use cases in basic and translational biomedical research. Biofunctionalized nanodiamond sensors can be specifically targeted enabling free radicals detection at the mitochondrial membrane or on the nucleus. Decorating viruses or bacteria with nanodiamonds helped to reveal free radicals load on surfaces of the pathogens and elucidate mechanisms of an immune response in in vitro cellular cultures.
- NDNV70nmHi10ml was selected by end users as optimal for detection of free radicals in live cells.
- Multicolor NDNV/NVN120nm1mg is recommended for multiplexed imaging and sensing.
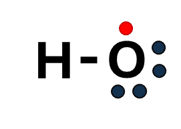
- NDNV10nmMd was used for detection of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by catalyzing production of radical intermediates.
Adamas’s products for use in T1 relaxometry: